Tells how drastically buyers will cut back or increase their demand for a good when the prices rise or fall.
Elastic Demand - When demand will change greatly given a small change in price Wants (ticket prices for movies increase then we are lead to find alternative ways) More than one
Inelastic Demand - Your demand for a product will not change regardless of price Needs(gasoline, salt, medicine) Less than one
Uni elastic Demand - Equal to one
- New quantity - old quantity/old quantity
- New price - old price/old price
- PED
Equilibrium:
The point at which the supply curve and demand curve intersect. This point they meet at shows that the resources are being used efficiently.
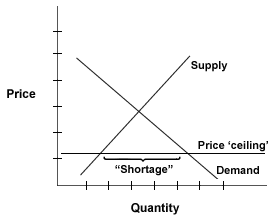
Shortage - QD>QS
Surplus - QS>QD
Price Ceiling:
Government imposed limit on how high you can be charged.
Price Floor:
Government price control on how low a price can be charged for a product.

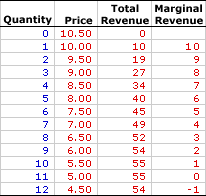
Total Revenue - Price x Quantity
Marginal Revenue - Additional income from selling an additional unit of a good
Fixed Cost - A cost that does not change no matter how much is produced (rent, mortgage)
Variable Cost - cost that changes and fluctuates (water bill - how much you use)
Marginal Cost - New total cost - old total cost spend the cost, revenue is what you bring in
Total Cost - TFC + TVC = TC
Average Total Fixed Cost - AFC + AVC
Average Fixed Cost - TFC/Quantity
Average Variable Cost - TVC/Quantity
Total Variable Cost - Quantity x AVC

No comments:
Post a Comment